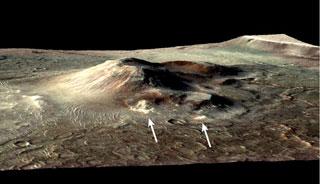
This volcanic cone in the Nili Patera caldera on Mars has hydrothermal mineral deposits on the southern flanks and nearby terrains. Photo: NASA
PASADENA (BNS): Scientists have found light-colored mounds of a mineral deposited on a volcanic cone more than three billion years ago on the surface of Mars.
According to NASA, these preserve evidence are the most recent habitable microenvironments on Mars.
The mineral is identified as hydrated silica by the by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
The mounds' composition and their location on the flanks of a volcanic cone provide the best evidence yet found on Mars for an intact deposit from a hydrothermal environment -- a steam fumarole, or hot spring.
Such environments may have provided habitats for some of Earth's earliest life forms.
"The heat and water required to create this deposit probably made this a habitable zone. If life did exist there, this would be a promising type of deposit to entomb evidence of it -- a microbial mortuary,” J.R. Skok of Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island and lead author of a paper about these findings said.
According to the findings, it is clear that at some times and in some places, Mars has had favorable environments for microbial life.
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit in 2007 had found concentrations of hydrated silica (nearly pure patch) on the surface of Mars.
"You have spectacular context for this deposit. It's right on the flank of a volcano. The setting remains essentially the same as it was when the silica was deposited," he added.
Observations by cameras on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter revealed patches of bright deposits near the summit of the cone, fanning down its flank, and on flatter ground in the vicinity.
Silica deposits around hydrothermal vents in Iceland are among the best parallels on Earth.
The volcanic activity that built the cone in Nili Patera appears to have happened more recently than the 3.7-billion-year or greater age of Mars' potentially habitable early wet environments recorded in clay minerals identified from orbit.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article












The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article